You may not even realize it, but you’re already using Artificial Intelligence?
Have you ever thought about how Instagram or any social media platform knows what kind of post you want to see next? Or how your phone’s camera can detect a smile and capture the ideal photo? That’s the magic of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in action.
The concept of Artificial Intelligence might remind you of Hollywood blockbuster science fiction films filled with robots and futuristic mayhem; you’re not the only one.
It has become one of the biggest buzzwords of all time.
But what if we told you it doesn’t have to be that complicated? This guide is here to be your translator.
We’re going to strip away the jargon and the hype to give you a clear, simple answer to the question: What is Artificial Intelligence ?
We’ll explore how it works, see where you’re already using it, and look at why it matters to you—all in plain, human terms. No prior experience needed.
Table of Contents
So, What is Artificial Intelligence, Really?
At its depth, Artificial Intelligence is the science that teaches computers to think, learn, and solve problems in a way that mimics human Intelligence.
It’s all about creating systems that can reason, understand, and improve from experience, rather than simply providing a result without understanding.
Now, if we put on our slightly more formal hats, the official definition is a bit more specific. AI is a big branch of computer science that focused on building smart machines capable of performe or execute tasks that have traditionally required human intelligence. This includes things like:
- Visual Perception: Detect’s a friend’s face in a photo.
- Speech Recognition: Understanding your command to Siri or Alexa.
- Decision-Making: A GPS calculating the fastest route through traffic.
- Language Translation: Instantly converting a webpage from Spanish to English.
But what is the difference between Artificial Intelligence and a regular computer program? The best way to understand it is with an real life examples.
The Calculator vs. The Child
Imagine a simple calculator app on your mobile. It follows rigid, pre-written instructions: If a mobile user presses ‘2’, then ‘+’, then ‘2’, you must display ‘4’.
Its results are remarkably quick and precise, yet it cannot perform tasks that it hasn’t been explicitly programmed to handle.
It can’t learn, it can’t adapt, and it certainly can’t tell you what a picture of a dog looks like.
That’s traditional software.
Now, imagine yourself guiding a child to identify a cat. You wouldn’t present the child with an long list of rules like, “If it has pointy ears AND whiskers AND fur, then it is a cat.”
That approach would be impractical and would lead to constant failures.
Instead, you show them pictures and point, saying, “This is a cat,” “That’s a cat, too,” and “This one is also a cat.” After seeing enough examples, the child’s brain starts to recognize the patterns on its own. They learn the concept of a cat.
That is how modern AI works. Instead of being given strict rules, an Artificial Intelligence system is “trained” on massive amounts of data (like thousands of cat photos), and it learns the patterns and rules for itself.
This ability to learn from examples, rather than being explicitly programmed for every single possibility, is the magic ingredient of Artificial Intelligence.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Actually Learn?
So, how does a computer go from being a dumb calculator to a smart assistant that can predict your next move? It’s not magic—it’s a combination of two key ingredients: massive amounts of data and clever algorithms designed to learn from that data.
The key idea to understand in this context is Machine Learning. It serves as the driving force behind much of the Artificial Intelligence you engage with on a daily basis.
Now, let’s explore the core technologies that enable AI to function.
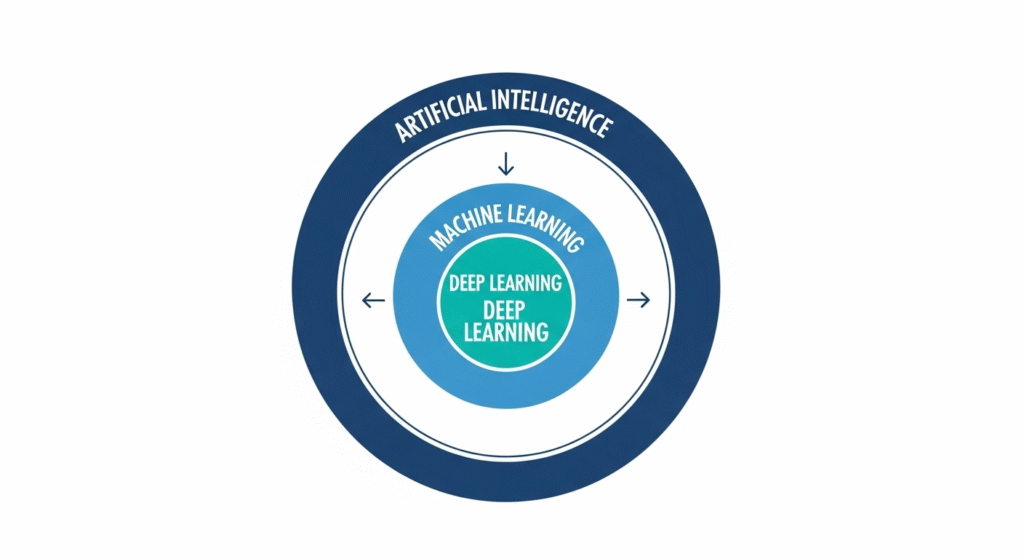
Machine Learning (ML): The Heart of Modern Artificial Intelligence
At its most basic, Machine Learning is the process of training a computer by showing it tons of examples, rather than programming it with explicit rules.
The algorithm analyzes this vast amount of data to identify patterns, which it then applies to forecast outcomes for new, previously unseen data.
For example, Think about your email’s spam folder. No one programmed your email service with a list of every possible spam phrase.
Instead, engineers fed a Machine Learning model millions of emails, some labeled “spam” and some labeled “not spam.”
The model analyzed everything and learned the tell-tale signs of junk mail on its own: suspicious links, urgent “BUY NOW!” language, odd formatting, and common misspellings.
Now, when a new email arrives, the AI can make an incredibly accurate prediction about whether it’s junk, even if it has never seen that exact email before.
Deep Learning (DL): The Next Level Up
If Machine Learning is the engine, think of Deep Learning as a high-performance, turbocharged version of machine learning.
Deep Learning represents a more sophisticated form of Machine Learning, that’s loosely inspired by the structure of the human brain.
It uses complex structures called “artificial neural networks” which have many layers, allowing it to analyze data deeply in detailed and identify far more subtle patterns.
A great example is how your phone or Google Photos can recognize specific people.
A Deep Learning model tackles this by breaking the problem down layer by layer:
Layer 1: It first learns to identify the most basic elements, like simple edges and areas of light and shadow.
Layer 2: It then combines those edges to form simple shapes like eyes, noses, and mouths.
Layer 3: It assembles those features into recognizable facial structures.
Final Layer: Finally, it can match that complete facial structure to a specific person’s face with high accuracy.
Each layer builds on the last, allowing the Artificial Intelligence to “see” and “understand” in a much more sophisticated way.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Teaching Computers to Understand Us
While ML and DL are about finding patterns in data, Natural Language Processing is a specialized field of AI cconcentrates on one thing: Connecting the divide between human language and computer comprehension.
It’s the technology that allows machines to read, interpret, understand, and even generate human text and speech.
For example, Every time you ask Siri for the weather, tell Alexa to play a song, or use Google Translate, you’re using NLP.
When a customer service chatbot on a website understands your typed question and gives a relevant answer, that’s NLP in action.
It’s what turns our messy, nuanced language into structured information a computer can work with.
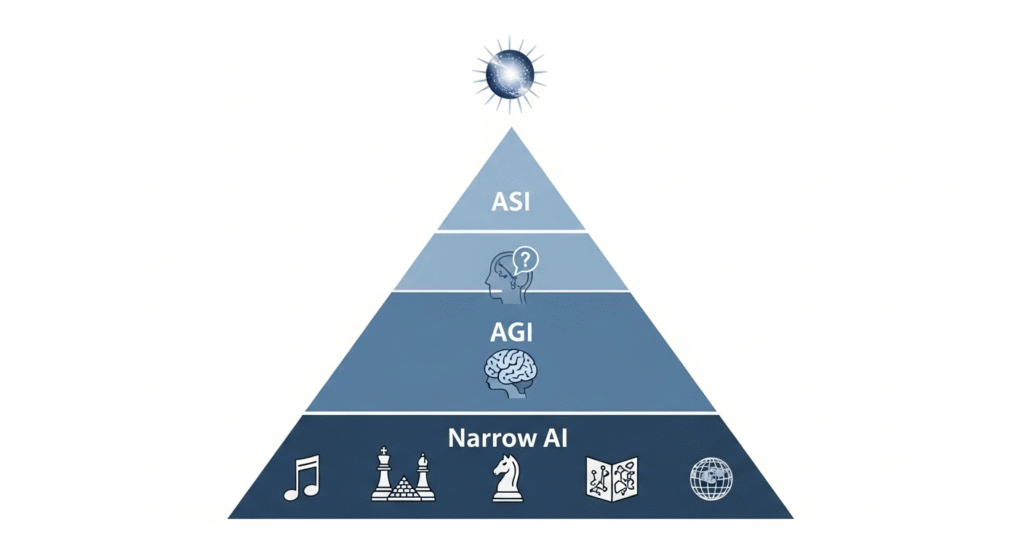
Different Types of AI: Not All AI is Created Equal
When you hear of the word ‘AI,’ your mind might jump straight to sentient machines from films such as The Terminator or a caring operating system as depicted in Her.
While that makes for great storytelling, it’s crucial to know that the Artificial Intelligence we see in science fiction is different from the AI that exists in our reality today.
To understand the difference between AI that exists in our reality and what is yet to come, specialists typically classify Artificial Intelligence based on its abilities.
This is the most important distinction for a beginners.
By Capability: What Can It Do?
Narrow AI (or Weak AI): The Specialist
This is the only type of AI that humanity has achieved so far. Narrow AI is an artificial intelligence that is designed and trained to perform one specific task.
It’s incredibly powerful within its limited context, but it can’t operate outside of its designated field. The AI that recommends music on Spotify can’t drive a car.
The AI that powers Google Translate can’t play chess. Every single AI application you use today, from Siri to your spam filter, is a form of Narrow AI.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): The Human-Level Thinker
This is the AI of science fiction. AGI refers to a hypothetical machine with the flexible, adaptable intelligence of a human being.
An AGI could understand, learn, and apply its intelligence to solve any problem, just like a person can.
It could learn to write a symphony, then switch to developing a scientific theory, then learn a new language.
It’s important to be clear: AGI does not exist yet. It remains the aspirational, long-term goal for many AI researchers.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): The Future Frontier
Taking it one giant leap further, ASI is a hypothetical AI that would not just match human intelligence, but greatly surpass it in every conceivable way—from scientific creativity and problem-solving to social skills.
This is a concept that raises profound philosophical and ethical questions, but for now, it remains firmly in the realm of speculation.
How Does Artificial Intelligence “Think”?
Apart from the classification of functions AI systems can perform, they can also be classified based on how they work.
That latter one is a bit more technical, but here is a short description of the two main types you will likely come across.
1. Reactive Machines:
The simplest AI type are reactive machines. It has no memory and is unable to use past experiences to make current decisions.
All it does is perceive the world and respond to it. They analyzed the pieces on the board and “brilliantly” made moves step-by-step without remembering the previous ones.
This is how IBM Deep Blue, the computer that made history for beating world chess champion Garry Kasparov, operated.
2. Limited Memory:
This is where most of the modern AI systems work – limited memory. These machines have the ability to look into the recent past to make a decision.
A good example of this would be a self-driving car. These cars continuously monitor the speed and direction of other cars around them (past information) to decide how to navigate during the present moment.
Also, your Netflix recommendations work using limited memory too; they check your latest viewed content.
AI in Your Daily Life: 7 Examples You See Every Day

Artificial Intelligence is not a technology of the future—it is already an integral part of your daily life routines.
Once you start searching for it, you will definitely find it everywhere. Here are seven examples where AI actively works in the background.
- STREAMING AND SHOPPING RECOMMENDATIONS
That “Recommended for You” section on Netflix, Amazon or Spotify is scarily accurate. It is based purely on AI.
These companies look into your listening and/or viewing history, check it against tens of millions of users, then suggest what you are most likely to enjoy next seamlessly.
- DIGITAL VOICE ASSISTANTS
Asking for weather updates from Siri, commanding Alexa to set a timer, or asking Google Assistant any question is actually using hi-tech Artificial Intelligence.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) permits these assistants to execute the tasks mentioned above.
- NAVIGATION & MAPS
Google Maps and Waze are more sophisticated than just showing you a static map.
They track real-time traffic, road conditions, and accidents, analyzing them with AI from millions of users. It then generates the most optimal journey for you, saving time and hassle.
- SOCIAL MEDIA FEEDS
Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook don’t serve you posts in real-time order. The AI builds a unique, customized experience for each user.
The algorithms look at your preferences, including likes, comments, shares, and even your dwell time on a post to guess what content will retain your attention the most.
- SPAM FILTERS & SMART REPLIES
Without AI, your email inbox would be a chaotic mess. Machine learning models filter out junk email as well as work consistently to identify the characteristics associated with email spam.
In addition, some services, like “Smart Reply” from Gmail, Artificial Intelligence analyzes the email text and automates logical short responses.
- CUSTOMER SERVICE CHATBOTS
A website’s customer service chatbot that uses NLP to understand and resolve user questions instantly provides real-time responses to FAQs for low-level customer service issues.
These bots address basic questions while more difficult problems are escalated to human agents.
- AI-POWERED PHOTOGRAPHY
We can recall times you have taken photos at night and wondered how your smartphone captured the details so perfectly.
Exposure control has advanced in the modern era, meaning a smartphone’s “night sight” and “portrait mode” Artificial Intelligence features smooth backgrounds, reduces noise, or stitches multiple images to produce an enhanced final image.
The Pros and Cons of Artificial Intelligence
Like any major technology, from the printing press to the internet, Artificial Intelligence offers many amazing opportunities but also comes with significant challenges.
To understand its impact, we must examine both aspects. It’s not about being an idealistic optimist or a fearful pessimist; it’s about being a realist.
The Promise
Automation and Efficiency: At its core, AI excels at managing repetitive, time-consuming tasks.
This not only means quicker work, but also allows humans to focus on our strengths: creativity, strategic thinking, and solving complex problems.
Solving Complex Problems: AI can examine huge datasets in ways humans cannot.
This speeds up breakthroughs in key areas like medical research, helping to identify diseases earlier, and climate science, where it can model intricate environmental changes.
Hyper-Personalization: We already see this in our entertainment, but the possibilities are much broader.
Imagine tailored learning plans for students, specific medical treatments based on a person’s genetic code, and experiences that perfectly match a user’s needs.
Enhanced Safety: AI systems can operate tirelessly in environments that are too risky for humans, like deep-sea exploration, disaster cleanup, or handling dangerous materials.
They are also essential for identifying financial fraud and cybersecurity threats in real-time.
The Perils
Job Displacement: Many people worry that AI will take over jobs currently done by humans.
Although some experts think AI will create new jobs, the shift could lead to serious economic and social issues.
The discussion is not just about lost jobs; it also focuses on making sure the workforce is ready for future roles.
Bias and Fairness: An AI system depends on the data it’s trained on. If that data shows existing social biases related to race, gender, or income, the AI will learn and even reinforce those biases.
This can result in unfair outcomes in important areas like hiring, loan applications, and criminal justice.
Privacy and Data Security: AI models need a lot of data to learn effectively. This raises important questions about our privacy.
How is our personal data collected, stored, and used to train these systems? Who has access to it, and are they keeping it safe?
The “Black Box” Problem: Sometimes, especially with complex Deep Learning models, an AI’s decision-making process can be so complicated that even its creators can’t fully explain how it reached a specific conclusion.
This lack of clarity, often referred to as the “black box” problem, is a big issue when AI is used for important decisions where understanding the reasoning behind outcomes is crucial.
The Future is Now: What’s Next for AI?
The pace of AI development is impressive. While we can’t perfectly predict the future, we can clearly see where this technology is headed.
This isn’t about flying cars and robot assistants, at least not yet. It’s about practical advancements that are already happening and are set to become common soon.
Here are a few of the most exciting developments to watch:
- Hyper-Personalized Medicine
Forget treatments that fit everyone. The next wave of medical breakthroughs will use AI to analyze your unique genetic code, lifestyle, and medical history.
This will allow doctors to move from reacting to illness to preventing it. Imagine getting treatment plans and medications designed just for you.
Picture an Artificial Intelligence predicting your risk of disease years before you show any symptoms.
- A Revolution in Scientific Discovery
AI is becoming a valuable research assistant. Scientists can now use Artificial Intelligence to sort through millions of research papers, analyze complicated data from experiments, and spot patterns that would take human teams years to find.
This is speeding up discoveries in fields like materials science, where new, stronger, or more sustainable materials are developed, and biology, where we understand the complex interactions within living cells.
- Truly Creative Tools
We’ve already seen AI generate striking images from text prompts. The next step is to use that creative power in other areas.
Soon, you’ll be able to describe a mood and an Artificial Intelligence will create a unique musical soundtrack for your video.
AI tools will help write, edit, and even generate realistic video clips, acting as a creative partner that enables artists, marketers, and hobbyists to realize their visions like never before.
- Smarter, Safer Autonomous Vehicles
While fully self-driving cars are not quite there yet, the Artificial Intelligence behind them is getting much smarter.
Future systems won’t just react to what’s around them; they will communicate with other vehicles and city infrastructure to anticipate traffic jams, prevent accidents before they happen, and navigate complex urban environments with remarkable precision.
The goal is a transportation system that is much safer, more efficient, and accessible to everyone.
How Can You Learn More? Your AI Journey Starts Here

Reading this handbook is step number one, but the adventure doesn’t have to stop here.
Learning the fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence is similar to learning the rules of a new game—once you begin to play, the fun really starts.
If you find yourself intrigued, here are a couple easy ways that you can continue to learn and participate in the world of AI.
Get Your Hands Dirty: Experiment with AI Tools
The best way to see what Artificial Intelligence can and can’t do is to try it for yourself. There are many of the most powerful tools available to anyone. Don’t be afraid; just dive in and have a go.
- For Text and Ideas: Try using a tool such as ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini. Ask it to assist you in writing an email, meal plan for a week, simplify a complicated subject, or even create a goofy poem. Observe where it shines and where it struggles.
- For Creative Images: Experiment with a tool such as Midjourney or Microsoft Designer. Describe a fictional scene—”a photorealistic astronaut on horseback on Mars”—and see the AI turn it into a picture. It’s an excellent way to understand how Artificial Intelligence sees language creatively.
Stay in the Know: Follow the Conversation
The Artificial Intelligence world speeds along at light speed, but you don’t have to read dense research papers to stay current. Identify a few trustworthy sources that suit your taste.
- Trustworthy Tech News: WIRED, The Verge, and MIT Technology Review all do an excellent job of reporting on what’s new in Artificial Intelligence in clear language.
- AI-Specific Newsletters: There are numerous great newsletters (such as The Neuron or Ben’s Bites) that bring the most relevant Artificial Intelligence news and send it to your mailbox in a bite-sized format.
- Official Blogs: For major announcements, cut out the middlemen and head to the source by reading the official blogs of big Artificial Intelligence labs such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic.
Dive a Little Deeper: Learn the Fundamentals (for Free)
If you wish to learn more about the mechanics of the magic, you do not have to sign up for a university degree. There are wonderful, beginner-level courses online, most of which are free to audit.
- Online Learning Sites: Visit sites such as Coursera, edX, and AiBlogFeed. Look for courses that have names such as “Introduction to AI,” “AI for Everyone,” or “Elements of AI.” These are actually created for individuals with non-technical backgrounds.
The one key point is to keep your mind open, be curious, and have questions. You now have the basic knowledge to just do that.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is AI the same as Machine Learning?
No. Machine Learning is a type of AI. Think of AI as the overall goal, and ML as one of the primary methods for achieving it.
Will AI take my job?
It’s more likely to change your job. AI will automate certain tasks, but it will also create new roles that require human oversight, creativity, and strategic thinking.
Is AI dangerous?
The technology itself isn’t inherently dangerous, but like any powerful tool, it can be used for malicious purposes. The real danger lies in issues like bias, privacy invasion, and lack of regulation, which is why ethical development is so important.
AI is a Tool, Not a Master
AI is Foundational Technology
Artificial Intelligence is no longer science fiction; it’s a core part of our modern world, actively reshaping everything from our daily routines to entire industries.
Your First Step to Confidence
🧭 Understanding the basics is the essential first step to navigating this new world with confidence and clarity.
“The goal of AI isn’t to replace human intelligence, but to augment it. The future isn’t about humans versus machines, but humans with machines.”